| Version 40 (modified by , 11 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
IRIS : developing a new node concept
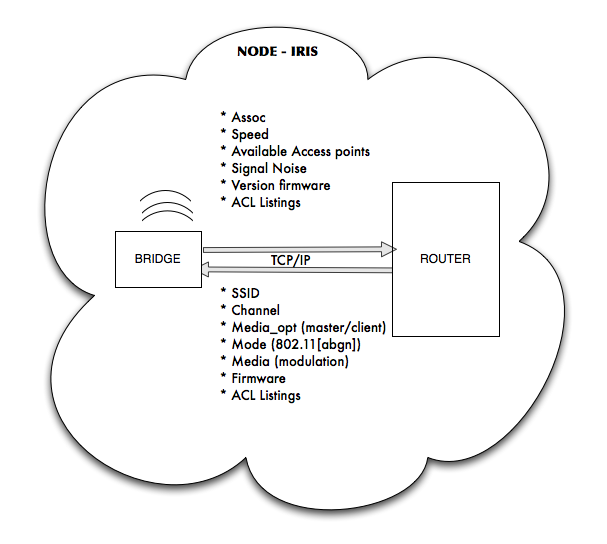
In the IRIS project we have developed a new node concept based on a separation of the 'radio interfaces' and the 'base node'.
The NanoBSD page is the place to be for up2date information on how to build/configure/create a WL node image. As always this project could use your help, by Contributing to various parts of the project.
The ConfigureBridge page shows you which bridges we use and how-to configure them. The WLCaptivePortal shows you how-to configure the captive portal software.
Concept
A node, type IRIS, is built using NanoBSD with some extensions a.o. to make package management a bit easier. Also the internet gateway (providing internet connectivity to the local wireless network) is based on NanoBSD.
The nodes are FreeBSD routers with DNS (bind), lvrouted as a dynamic internal routing daemon, thttpd webserver and a python based captive portal based on pf and tcpserver for the plain HTTP-redirects. Moreover there are some additions which are essential for large scale network monitoring such a nagios plugins and bandwith measurment tools (iperf).
A proxy gateway is a http-proxy based on tinyproxy and an authorative DNS server (bind). Included is also
reverse ssh-tunneling (for remote management behind NAT firewalls). Nodes use pen with a home-build pen-wrapper to select the 'best' proxy (i.e. the highest bandwith). An alternative is a packet filtering firewall using pf to allow only port 80, 443 rate limited traffic. Packet filtering gateways use lvrouted to advertise a default route.
Pilot
Tim Baas, student at Hogeschool Leiden prototyped the software as his afstudeerwerk. His documentation is available in the svn projects iris-directory (in Dutch). See also the youtube video's for the initial pilot description:
Roll out
Since 2009 we have revamped our nodes (a couple still left to be modified in 2015) and also built a lot of new ones. As of August 2014 the total number of iris nodes amounts to 103. We have chosen the following hardware configuration:
- nodemachine based on a
ALIX2D3board with1 - 2 GBcompact flash card containing the software. 802.11ainterlinks based on Ubiquity NanoStation5, NanoStationM5, BulletM5, NanobridgeM5.- Local accesspoint with 8 dB omni antenna and Atheros CM9 MiniPCI wireless card, or NanostationM2, NanostationM2-Loco.
- Optional: NanostationM2 or NanostationM2-Loco in repeater mode of local accesspoints to extend range of accesspoint network.
- Optional: unmanaged switch to allow connections of multiple vNanostationM2 or NanostationM2-Loco local accesspoints.
- PowerSupply gives you a hint on which power supply to use.
- AlixAPU Development started to use the Alix APU System board in the future.
- DCtoDCconverter gives you details about various DC conversions we apply.
Some youtube video's about building iris-type nodes:
- Bouw node Rijneke Boulevard
- Bouw node VdSterre
- Bouw node Juffermans
- Bouw node StJan
- Bouw node Meerburgkerk
- Bouw node Stenhuis
- Configuring a Nanostation
A 'howto' guide for building nodes is available in Dutch: Kookboek_Nodebouw.
Open Tickets
Starting Points for Trac
- TracGuide -- Built-in Documentation
- The Trac project -- Trac Open Source Project
- Trac FAQ -- Frequently Asked Questions
- TracSupport -- Trac Support
For a complete list of local wiki pages, see TitleIndex.
Attachments (2)
-
logo-nodefactory.png
(10.5 KB
) - added by 17 years ago.
Logo for Trac project nodefactory
- node-iris-connector-specs.png (75.8 KB ) - added by 14 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip